

The EU Japan Centre is releasing a weekly press review covering Japan's economic and business matters.
▶ Japan to issue Vietnam $10bn in yen loans for rail lines, gas plant
14 Feb, 2026
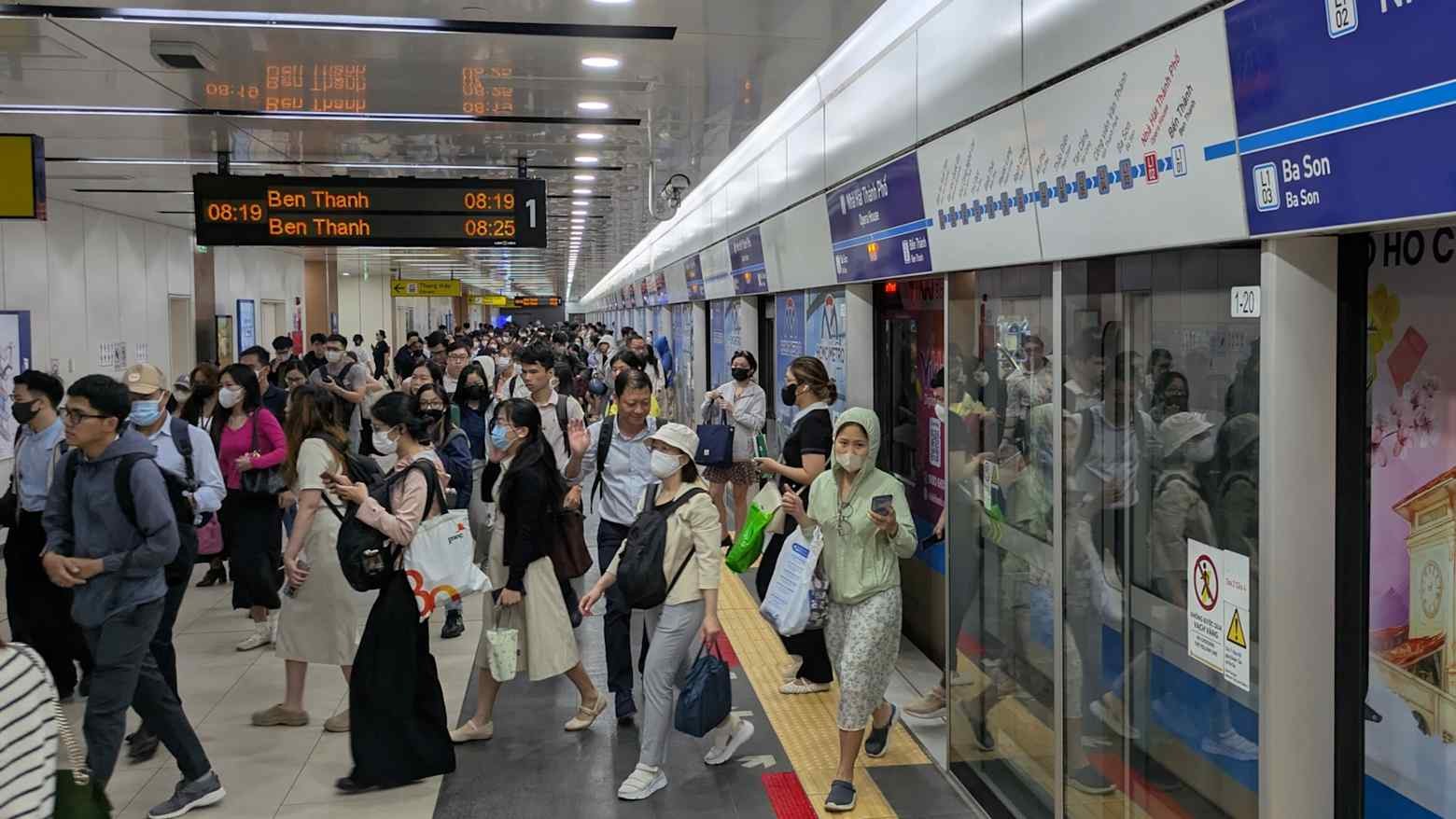 Photo Source: Yuji Nitta/Nikkei
Photo Source: Yuji Nitta/Nikkei
Japan plans to provide over $10 billion in yen loans to Vietnam over the next five years to fund infrastructure projects such as subways and gas-fired power plants, supporting Vietnam’s rapid growth and creating opportunities for Japanese companies. Key projects include Hanoi Metro Line 2, Ho Chi Minh City Metro Line 1 extensions, and the O Mon 3 gas plant. Japan’s loans, part of its ODA program, are long-term and low-interest. While Vietnam’s high growth and public investment needs make foreign financing critical, challenges like complex administrative procedures and policy opacity must be addressed to ensure Japanese company participation.
▶ Japan to Strictly Control Exports of Lethal Defense Equipment While Mulling Expanding Exports’ Range
15 Feb, 2026
 Photo Source: Yomiuri
Photo Source: Yomiuri
Japan’s government and ruling LDP are considering revising the Three Principles on Transfer of Defense Equipment and Technology to expand and better control defense exports. The current “five-category” limit—covering only rescue, transport, vigilance, surveillance, and minesweeping—is likely to be removed, potentially allowing exports of highly lethal weapons like tanks, missiles, and fighter jets. Exports would be classified by lethality, with Cabinet-level approval via the National Security Council required for highly lethal items, while less lethal equipment could be approved administratively. Export destinations would be limited to countries with Japan’s defense transfer agreements, ensuring compliance with the U.N. Charter.
Yomiuri:https://japannews.yomiuri.co.jp/politics/defense-security/20260215-311490/
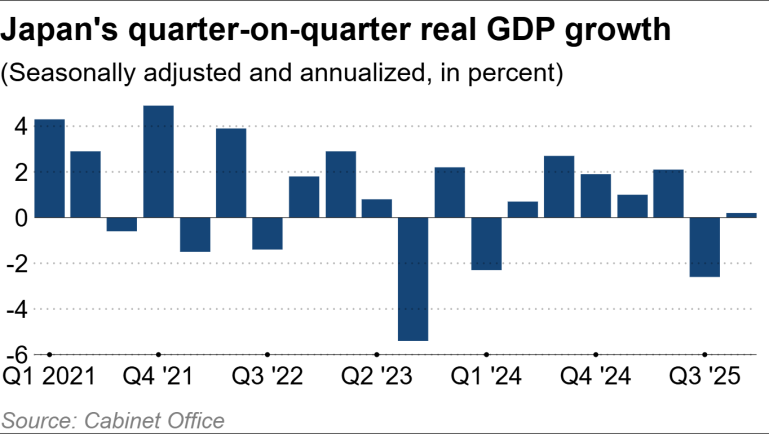
▶ Japan Q4 2025 GDP grows annualized 0.2%, below expectations
16 Feb, 2026
 Source: Cabinet Office
Source: Cabinet Office
Japan’s economy grew just 0.1% in the October–December quarter (0.2% annualized), far below expectations, following a sharp contraction in the previous quarter. Weak private consumption and falling exports weighed on growth, although business investment was slightly stronger than expected. Despite stock market gains, households continue to struggle with inflation and negative real wages, while the Bank of Japan balances rate hikes with economic support. The outlook remains modest, with economists forecasting moderate growth in early 2026.
Nikkei Asia:https://asia.nikkei.com/economy/japan-q4-2025-gdp-grows-annualized-0.2-below-expectations
▶ Japan eases screening for US-made cars in boost for Toyota's reverse imports
17 Feb, 2026
 Photo Source: Azusa Kawakami/Nikkei
Photo Source: Azusa Kawakami/Nikkei
Japan will introduce a simplified safety screening system for U.S.-made vehicles, allowing certification based on U.S. documentation without additional testing. The move supports Japanese automakers such as Toyota, Honda and Nissan, which are considering reverse-importing U.S.-built models into Japan. The change aims to ease trade friction with the U.S. and could help automakers expand sales of high-margin vehicles in the Japanese market.
▶ AI Agents Should Consult Humans, Say New Rules from Japanese Govt
17 Feb, 2026
 Image: Reuters
Image: Reuters
Japan is updating its AI guidelines to require human oversight in autonomous systems, including robots, self-driving vehicles, and AI agents that perform tasks independently. The draft revisions, issued by the Internal Affairs and Communications Ministry and the Economy, Trade and Industry Ministry, introduce clear definitions for “physical AI” and “AI agents” and call for safeguards to prevent malfunctions or misuse, such as obtaining consent for high-value transactions. While nonbinding, these guidelines signal Japan’s proactive approach to responsible AI deployment and could influence global standards. Final revisions are expected by the end of March.
Yomiuri:https://japannews.yomiuri.co.jp/politics/politics-government/20260217-311850/
▶ Japan's exports jump 16.8% in January on strong Asia demand
18 Feb, 2026
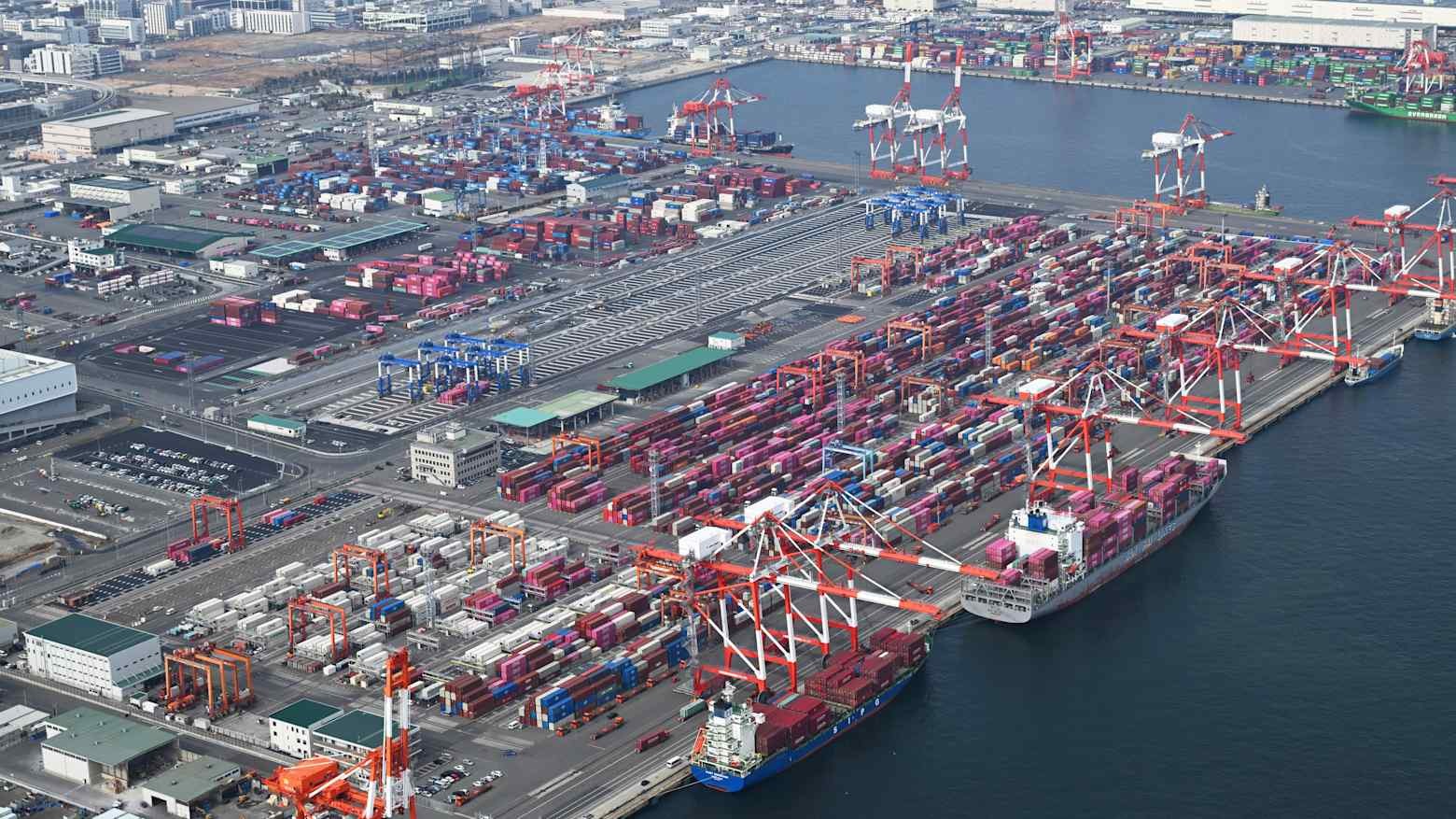 Photo Source: Yo Inoue/Nikkei
Photo Source: Yo Inoue/Nikkei
Japan’s exports rose 16.8% year-on-year in January, marking a fifth straight month of growth and beating market expectations, driven mainly by strong demand from China. However, exports to the U.S. declined, and imports fell 2.5%, resulting in a smaller-than-expected trade deficit of 1.15 trillion yen. Despite improving trade data, Japan’s economic recovery remains fragile, with hopes that domestic consumption and wage growth will support further momentum.
Nikkei Asia:https://asia.nikkei.com/economy/trade/japan-s-exports-jump-16.8-in-january-on-strong-asia-demand
▶Japan scoops up seabed mud, raises hopes for rare earth supply
18 Feb, 2026
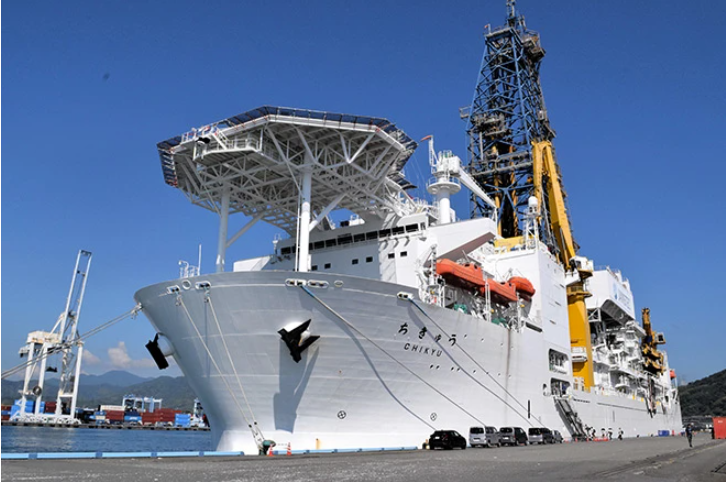 Photo Source: Asahi
Photo Source: Asahi
A Japanese research team successfully lifted seabed mud 5,700 meters deep near Minami-Torishima that may contain rare earth elements, marking the world’s first attempt at such extreme ocean depths. The project, led by JAMSTEC under the Strategic Innovation Promotion Program, aims to reduce Japan’s dependence on China for critical rare earths used in high-tech products like EV motors, wind turbines, and military equipment. A full-scale mining test is planned for February 2027, but challenges remain, including developing deep-sea extraction, smelting, and environmentally safe refining techniques. Japan hopes this initiative will strengthen economic security and high-tech manufacturing independence.
Asahi:https://www.asahi.com/ajw/articles/16329095
▶ Japan's debt-servicing costs seen taking up 30% of budget in 3 years
18 Feb, 2026
 Photo Source: Akira Kodaka/Nikkei
Photo Source: Akira Kodaka/Nikkei
Japan’s debt-servicing costs are projected to rise to 41.3 trillion yen by fiscal 2029, accounting for 30% of the national budget, as interest rates increase. Higher bond yield assumptions will push interest payments to 21.6 trillion yen, significantly up from fiscal 2026 levels. While tax revenue growth is expected to produce a primary surplus, rising debt costs will put increasing pressure on overall government spending.
▶ Japan to offer support for exports of flexible perovskite solar cells
18 Feb, 2026
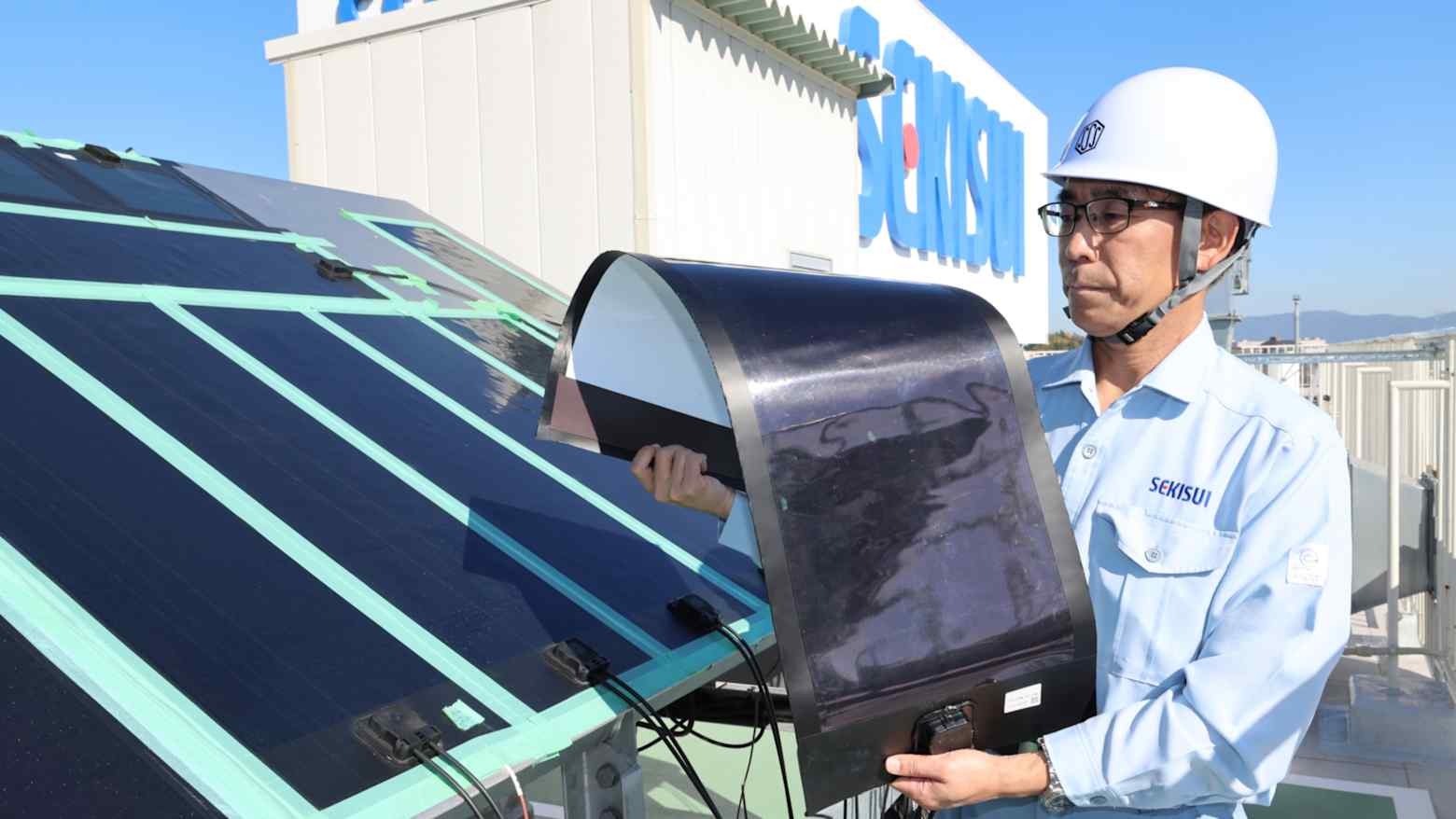 Photo Source: Kosaku Mimura/Nikkei
Photo Source: Kosaku Mimura/Nikkei
Japan plans to offer subsidies from fiscal 2026 to support overseas installations of flexible perovskite solar cells, aiming to promote a homegrown renewable energy technology with global potential. Demonstration projects are envisioned in countries such as Indonesia, Thailand, the U.S., and Germany to build track records and expand export channels. The initiative, part of the government’s growth strategy under Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi, complements domestic support measures. Meanwhile, Sekisui Chemical plans to begin mass production in fiscal 2027, potentially giving Japanese firms a competitive advantage.
Nikkei Asia: https://asia.nikkei.com/business/energy/japan-to-offer-support-for-exports-of-flexible-perovskite-solar-cells
▶ Japan gov't panel approves 2 iPS-derived drugs in global first
19 Feb,2026
 Photo Source: Kyodo
Photo Source: Kyodo
Japan’s health ministry has approved the world’s first commercial regenerative medicines derived from iPS cells: ReHeart by Cuorips for severe heart failure, and Amchepry by Sumitomo Pharma and Racthera for Parkinson’s disease. ReHeart uses heart muscle sheets to promote blood vessel formation and restore heart function, while Amchepry injects dopaminergic neural progenitor cells to improve motor function by replenishing dopamine. Both therapies build on Shinya Yamanaka’s Nobel-winning iPS cell technology.
Kyodo:https://english.kyodonews.net/articles/-/70874
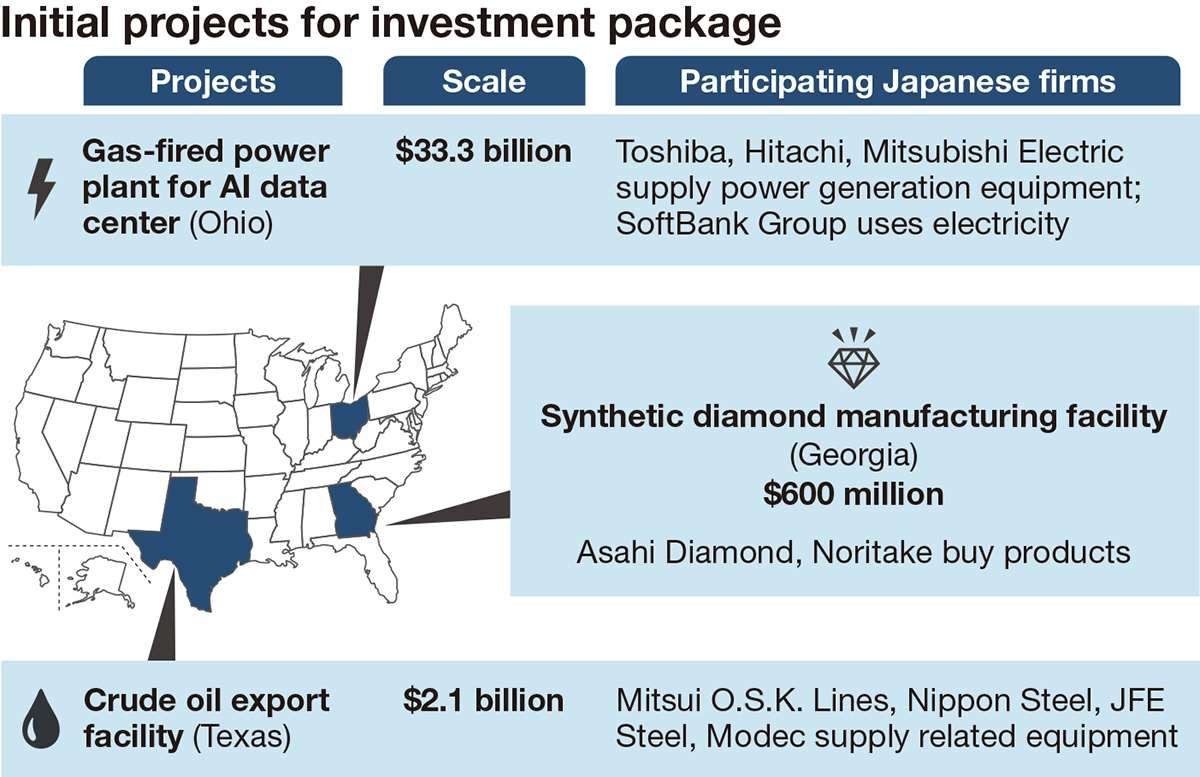
▶ Japan, U.S. Name 3 Inaugural Investment Projects; Reached Agreement After Considerable Difficulty
20 Feb, 2026
 Source: Yomiuri
Source: Yomiuri
Japan and the United States have selected three inaugural projects to launch a $550 billion investment package in the U.S., with $36 billion allocated to the first projects. The initiatives focus on economic security and include a gas-fired power plant in Ohio (led by SoftBank, with Toshiba and Hitachi supplying equipment), a crude oil export facility in Texas (involving Mitsui O.S.K. Lines and Nippon Steel), and a synthetic diamond manufacturing plant in Georgia (with Asahi Diamond Industrial participating). Funding will come from the Japan Bank for International Cooperation and Japanese banks, with the U.S. providing land and permitting support. Profits will be shared 50-50 up to loan repayment, then predominantly to the U.S. The projects aim to strengthen supply chains, diversify sources, and serve as a model for future investment.
Yomiuri:https://japannews.yomiuri.co.jp/business/economy/20260220-312340/
▶ Pivoting solar panels balance power needs with farming in Japanese paddies
20 Feb, 2026
 Photo Source: Idemitsu Kosan
Photo Source: Idemitsu Kosan
Idemitsu Kosan has launched its first large-scale agrivoltaics project, installing solar panels over a 3-hectare rice paddy in Tokushima prefecture. The facility generates about 2,500 MWh annually while maintaining normal rice production levels, using adjustable panels to balance sunlight for crops and power output. Agrivoltaics is gaining attention in Japan as suitable land for conventional solar farms declines and the government targets 40–50% renewable electricity by 2040. The system provides farmers with additional rental income, though concerns remain about environmental and landscape impacts.
Nikkei Asia: https://asia.nikkei.com/business/energy/pivoting-solar-panels-balance-power-needs-with-farming-in-japanese-paddies
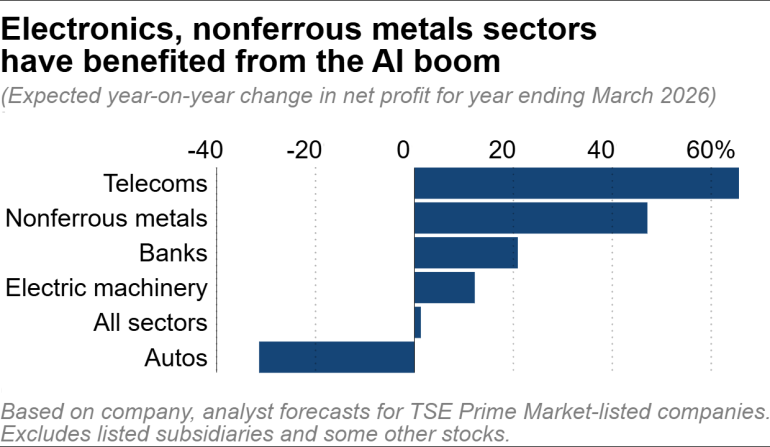
▶ Japan-listed companies set to eke out 5th straight year of record profits
20 Feb, 2026
 Source: Nikkei
Source: Nikkei
Japanese listed companies on the Tokyo Stock Exchange Prime Market are set to extend a five-year streak of record profits, helped by asset sales, AI-related investments, and stronger consumer spending. Net profits are projected to rise 1% for the fiscal year ending March, with margins at 6.3%. Capital efficiency efforts, such as selling noncore businesses, have improved ROE, with over 60% of companies exceeding the TSE’s 8% target. Rising stock prices and strong cash reserves provide room for shareholder returns, while continued semiconductor investment, easing U.S. tariffs, and higher interest rates support future earnings growth. Nonfinancial firms hold over ¥110 trillion in cash, and wage increases of 5% or more are expected for the third consecutive year.
Nikkei Asia: https://asia.nikkei.com/business/companies/japan-listed-companies-set-to-eke-out-5th-straight-year-of-record-profits
▶ Japan's January consumer prices grow at slowest pace in 2 years
20 Feb, 2026
 Photo Source: Mao Kawano/Nikkei
Photo Source: Mao Kawano/Nikkei
Japan’s core consumer prices rose 2.0% in January from a year earlier, marking the slowest increase in two years, mainly due to lower energy costs after the provisional gasoline tax was scrapped. While food prices remained high, overall inflation eased from December’s 2.4% rise. The slowdown has drawn attention to the Bank of Japan’s next rate decision, after it raised interest rates to 0.75% in December.
Nikkei Asia:https://asia.nikkei.com/economy/japan-s-january-consumer-prices-grow-at-slowest-pace-in-2-years
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
▶ Japan's Sojitz to expand Australian rare earth imports
16 Feb, 2026
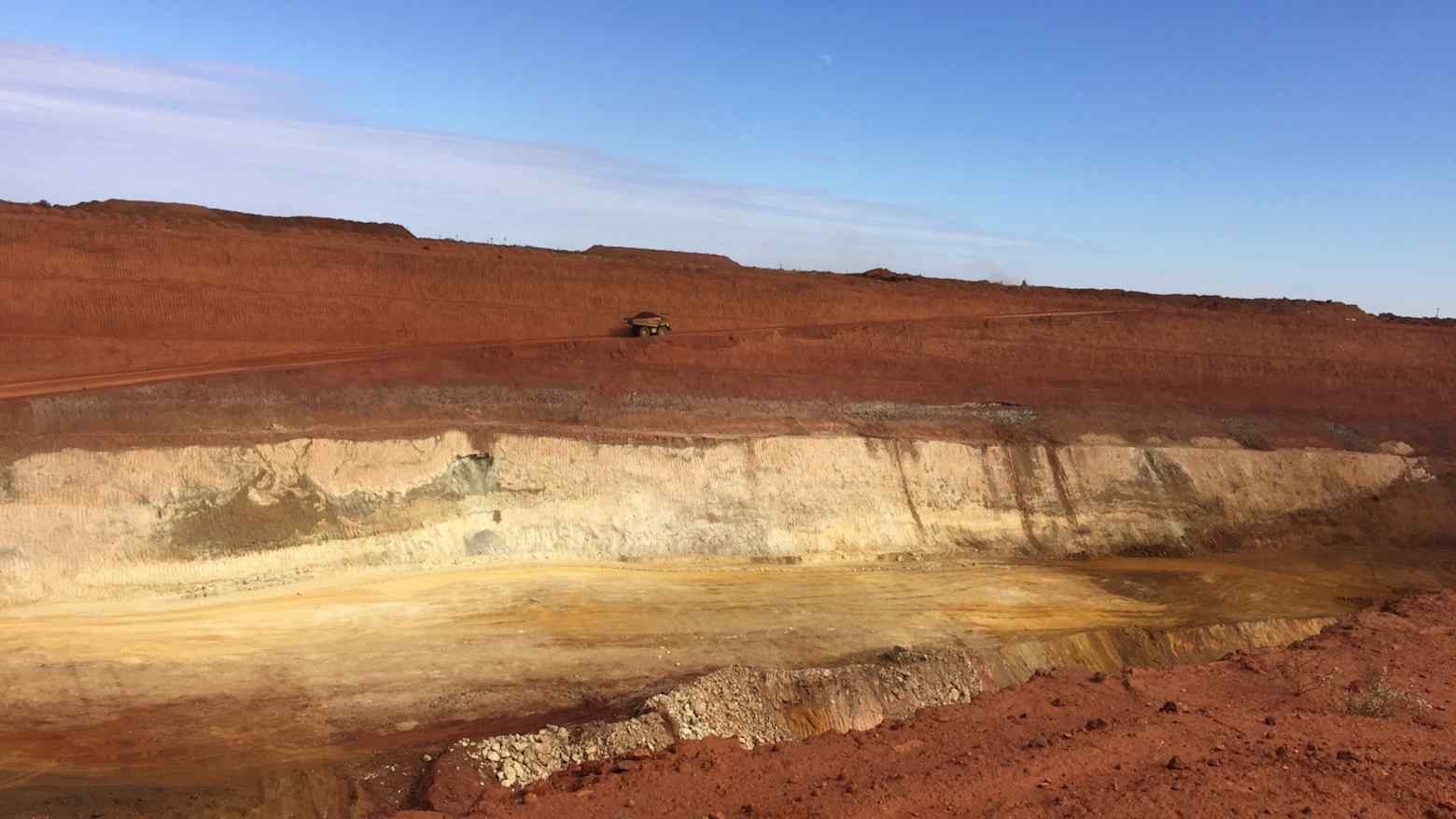 Photo Source: Reuters
Photo Source: Reuters
Japanese trading house Sojitz will expand imports of Australian medium to heavy rare-earth elements, starting with samarium in April, and aims to increase its portfolio from two to six elements by mid-2027. This move reduces Japan’s reliance on China for critical minerals used in high-tech industries, including permanent magnets for fighter jets, nuclear reactors, and EV motors. Imports will come from Lynas Rare Earths’ new separation facility in Malaysia, marking the first commercial production of samarium outside China. Sojitz and JOGMEC have invested in Lynas to secure supplies of light and heavy rare earths, while cost and profitability remain challenges for sourcing medium to heavy elements outside China.
Nikkei Asia:https://asia.nikkei.com/business/materials/japan-s-sojitz-to-expand-australian-rare-earth-imports
▶Yanmar Takes a Major Step Toward a Low-Carbon Marine Future
16 Feb, 2026
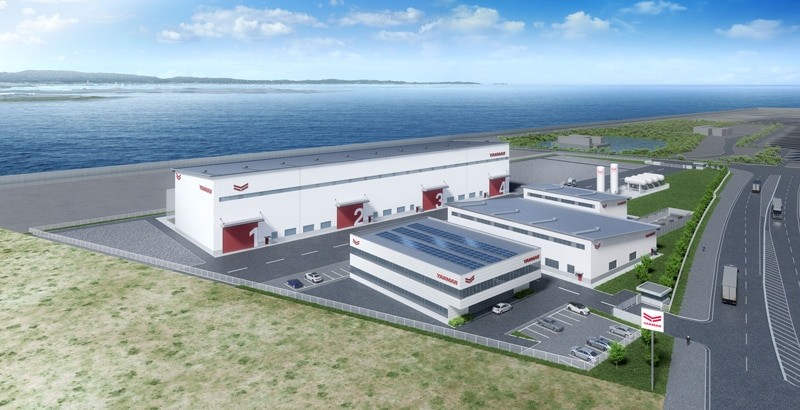 Image: Yanmar
Image: Yanmar
Yanmar Power Solutions plans to build a new factory at its Phoenix site in Amagasaki, Hyogo, to develop and test next-generation engines compatible with hydrogen, methanol, and ammonia. Scheduled to start operations around March 2029, the facility will strengthen production systems for marine and land-use engines, supporting decarbonization and the marine industry’s goal of carbon neutrality by 2050.
Yanmar:https://www.yanmar.com/global/marinecommercial/news/2026/02/16/161526.html
▶ Toyota, Honda face fuel cell car slump as hydrogen stations retreat
18 Feb, 2026
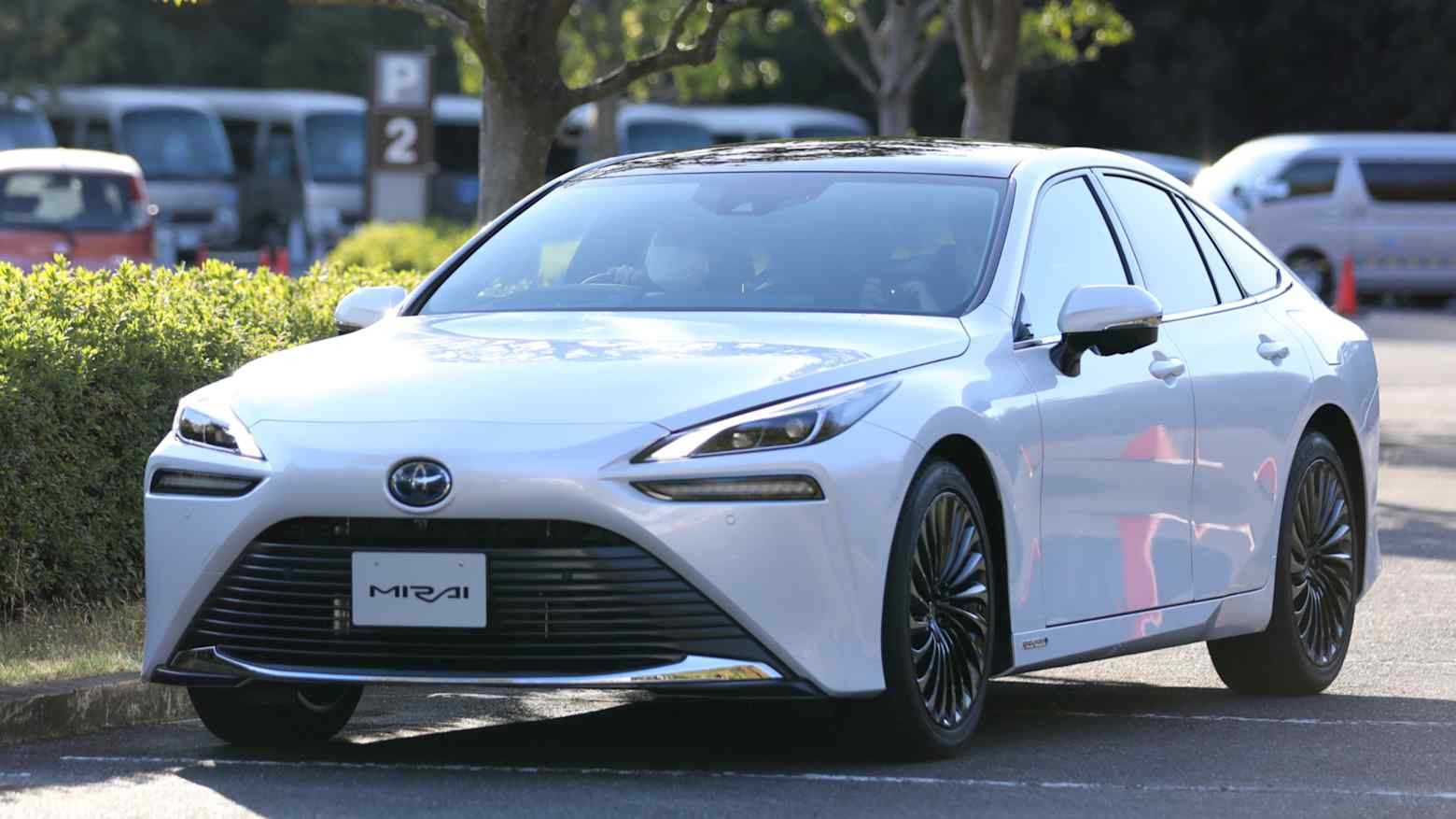 Photo Source: Koji Uema/Nikkei
Photo Source: Koji Uema/Nikkei
Hydrogen vehicle infrastructure in Japan is shrinking, with the number of refueling stations down 10% from 2021 and far below government targets. As a result, fuel-cell vehicle (FCV) sales have plunged 83% since 2021, with high vehicle costs and limited station availability discouraging buyers. Many stations are unprofitable due to low usage and high construction and operating costs, leading operators to shut them down. Similar pullbacks are occurring overseas, with energy companies and automakers scaling back hydrogen projects. While Toyota and other manufacturers continue investing in hydrogen technology, the future of FCVs depends on whether a sustainable hydrogen supply chain and infrastructure can be built.
Nikkei Asia: https://asia.nikkei.com/business/automobiles/toyota-honda-face-fuel-cell-car-slump-as-hydrogen-stations-retreat
▶ Renesas teams with US-based GlobalFoundries to make next-gen auto chips
18 Feb, 2026
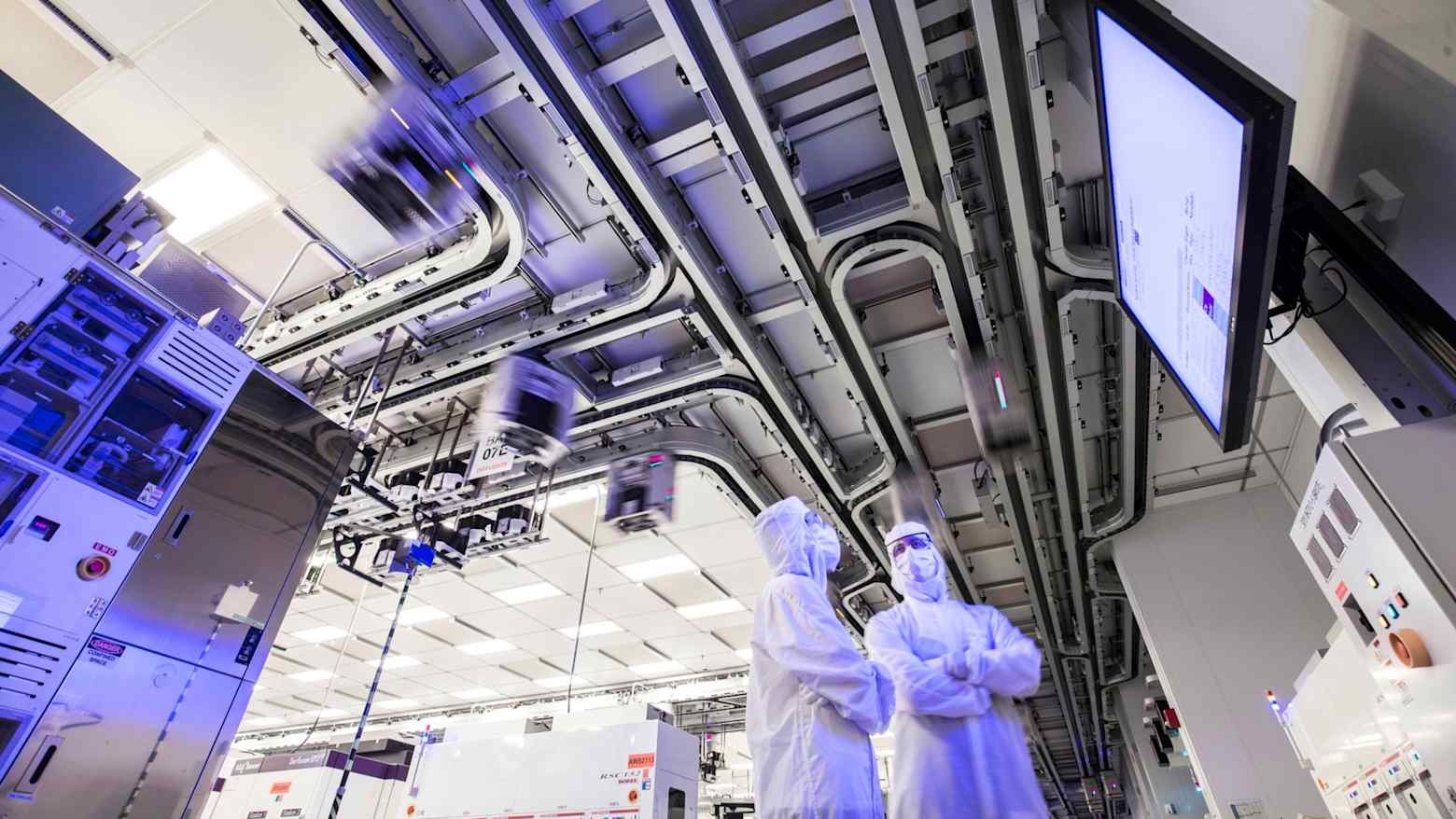 Photo Source: GlobalFoundries
Photo Source: GlobalFoundries
Renesas Electronics and U.S.-based GlobalFoundries (GF) will jointly produce semiconductors for next-generation vehicles, with production starting around mid-2026 at GF facilities in the U.S., Germany, Singapore and China. Renesas will design chips for advanced driver-assistance systems and EVs, while GF will handle manufacturing. The companies are also considering transferring GF’s 12–28 nm manufacturing technology to Renesas’ plants in Japan, potentially enabling the production of more advanced automotive logic chips. The partnership supports demand for high-performance, power-efficient semiconductors suited to next-generation vehicles.
▶ The innovations at the heart of next-gen AGTs
18 Feb, 2026
 Image: MHI
Image: MHI
The Prismo automated guideway transit system by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries uses onboard regenerative batteries that recharge at stops and during braking. This eliminates the need for continuous power rails, improves energy efficiency by 10%, and allows for a slimmer, simpler AGT design while reducing the risk of passengers being stranded during power outages.
MHI Video footage available):
https://spectra.mhi.com/smart-infrastructure/the-innovations-at-the-heart-of-next-gen-agts
▶ Local players join Tesla's quest to dominate EV charging in Japan
19 Feb, 2026
 Photo Source: Hana Slevin Ohama/Nikkei
Photo Source: Hana Slevin Ohama/Nikkei
Tesla’s North American Charging Standard (NACS) is gaining traction in Japan as automakers like Mazda (from 2027) and Sony Honda Mobility, as well as European brand Stellantis, plan to adopt it, despite CHAdeMO remaining the dominant national standard. The move aims to improve customer convenience, reduce development costs, and align with the U.S. market, a key region for Mazda. Tesla leads Japan’s EV market with fast charging (up to 250 kW), outpacing domestic models. Charging operators are also preparing NACS-compatible stations, while CHAdeMO is updating its systems to improve usability. Tesla seeks to make NACS the de facto standard in Japan.
▶ Successful Achievement of 20MPaG Discharge Pressure in a Process Gas Compressor Required for Commercial CCUS to Advance Decarbonization
20 Feb, 2026
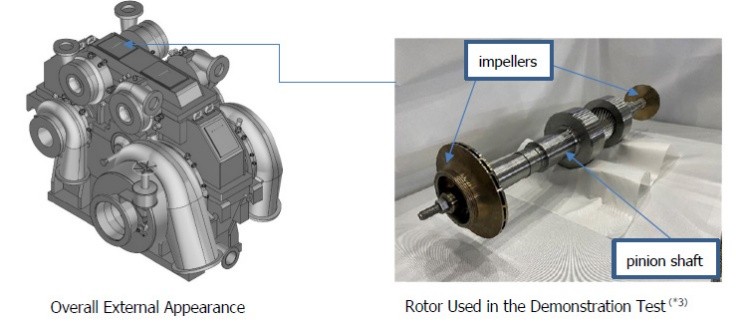 Image: IHI
Image: IHI
IHI Corporation and its subsidiary IHI Rotating Machinery Engineering successfully tested a process gas compressor using CO₂, achieving a maximum discharge pressure of 20 MPaG. This enables the injection of supercritical CO₂ into deep geological formations like saline aquifers, advancing commercial CCUS and industrial decarbonization. The demonstration used a turbo-type, multi-shaft, multi-stage compressor with geared impellers for optimized efficiency. IHI plans to expand these compression technologies across CCUS and other decarbonization processes, enhancing system reliability and supporting low-carbon infrastructure development.
IHI:https://www.ihi.co.jp/en/all_news/2025/industrial_general_machine/1201879_13741.html
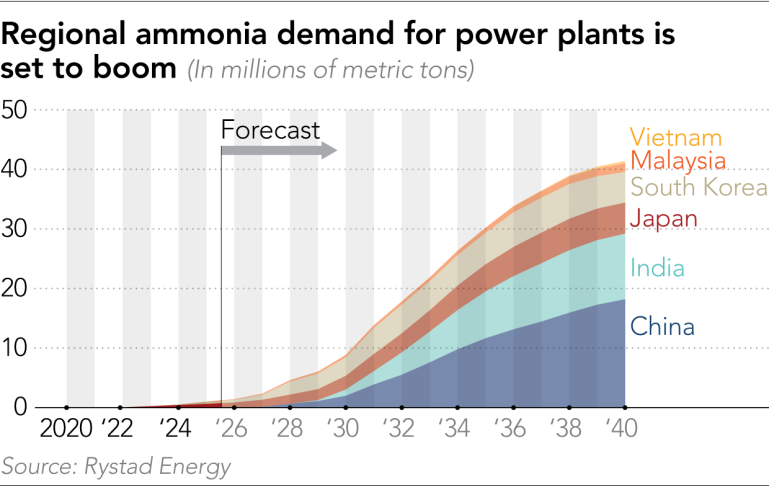
▶ How burning ammonia in power plants may help Japan to net-zero emissions
20 Feb, 2026
 Source: Rystad Energy
Source: Rystad Energy
Japan’s largest coal-fired power plant, the Hekinan Thermal Power Station, is building four 40-meter ammonia storage tanks to co-fire low-carbon ammonia with coal, starting with 20% substitution in 2029 and gradually increasing to reduce carbon emissions. Ammonia does not emit CO₂ when burned, offering a way to decarbonize coal-fired plants while maintaining energy supply. The project is supported by the government through subsidies, but challenges remain, including high costs, supply chain development, and environmental concerns about prolonging coal use. Despite these issues, ammonia co-firing is seen as a practical short-term solution for Japan’s energy transition.
Published: February 2026
The EU-Japan Centre currently produces 5 newsletters :









